Transformers documentation
SegFormer
This model was released on 2021-05-31 and added to Hugging Face Transformers on 2021-10-28.

SegFormer
SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers is a semantic segmentation model that combines a hierarchical Transformer encoder (Mix Transformer, MiT) with a lightweight all-MLP decoder. It avoids positional encodings and complex decoders and achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks like ADE20K and Cityscapes. This simple and lightweight design is more efficient and scalable.
The figure below illustrates the architecture of SegFormer.
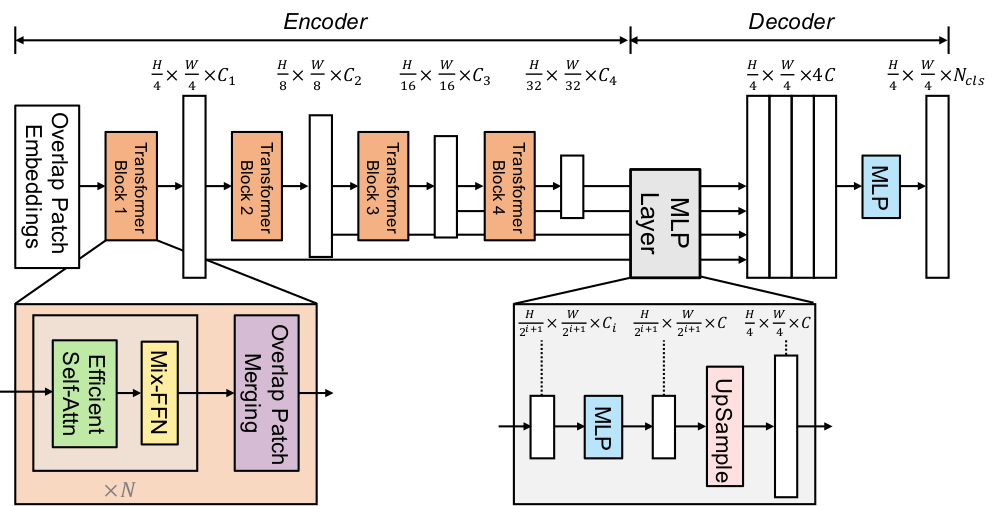
You can find all the original SegFormer checkpoints under the NVIDIA organization.
This model was contributed by nielsr.
Click on the SegFormer models in the right sidebar for more examples of how to apply SegFormer to different vision tasks.
The example below demonstrates semantic segmentation with Pipeline or the AutoModel class.
import torch
from transformers import pipeline
pipeline = pipeline(task="image-segmentation", model="nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipeline("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg")Notes
SegFormer works with any input size, padding inputs to be divisible by
config.patch_sizes.The most important preprocessing step is to randomly crop and pad all images to the same size (such as 512x512 or 640x640) and normalize afterwards.
Some datasets (ADE20k) uses the
0index in the annotated segmentation as the background, but doesn’t include the “background” class in its labels. Thedo_reduce_labelsargument inSegformerForImageProcessoris used to reduce all labels by1. To make sure no loss is computed for the background class, it replaces0in the annotated maps by255, which is theignore_indexof the loss function.Other datasets may include a background class and label though, in which case,
do_reduce_labelsshould beFalse.
from transformers import SegformerImageProcessor
processor = SegformerImageProcessor(do_reduce_labels=True)Resources
- Original SegFormer code (NVlabs)
- Fine-tuning blog post
- Tutorial notebooks (Niels Rogge)
- Hugging Face demo space
SegformerConfig
class transformers.SegformerConfig
< source >( num_channels = 3 num_encoder_blocks = 4 depths = [2, 2, 2, 2] sr_ratios = [8, 4, 2, 1] hidden_sizes = [32, 64, 160, 256] patch_sizes = [7, 3, 3, 3] strides = [4, 2, 2, 2] num_attention_heads = [1, 2, 5, 8] mlp_ratios = [4, 4, 4, 4] hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 classifier_dropout_prob = 0.1 initializer_range = 0.02 drop_path_rate = 0.1 layer_norm_eps = 1e-06 decoder_hidden_size = 256 semantic_loss_ignore_index = 255 **kwargs )
Parameters
- num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels. - num_encoder_blocks (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The number of encoder blocks (i.e. stages in the Mix Transformer encoder). - depths (
list[int], optional, defaults to[2, 2, 2, 2]) — The number of layers in each encoder block. - sr_ratios (
list[int], optional, defaults to[8, 4, 2, 1]) — Sequence reduction ratios in each encoder block. - hidden_sizes (
list[int], optional, defaults to[32, 64, 160, 256]) — Dimension of each of the encoder blocks. - patch_sizes (
list[int], optional, defaults to[7, 3, 3, 3]) — Patch size before each encoder block. - strides (
list[int], optional, defaults to[4, 2, 2, 2]) — Stride before each encoder block. - num_attention_heads (
list[int], optional, defaults to[1, 2, 5, 8]) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in each block of the Transformer encoder. - mlp_ratios (
list[int], optional, defaults to[4, 4, 4, 4]) — Ratio of the size of the hidden layer compared to the size of the input layer of the Mix FFNs in the encoder blocks. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported. - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler. - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - classifier_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability before the classification head. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - drop_path_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability for stochastic depth, used in the blocks of the Transformer encoder. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-06) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - decoder_hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — The dimension of the all-MLP decode head. - semantic_loss_ignore_index (
int, optional, defaults to 255) — The index that is ignored by the loss function of the semantic segmentation model.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a SegformerModel. It is used to instantiate an SegFormer model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the SegFormer nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import SegformerModel, SegformerConfig
>>> # Initializing a SegFormer nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512 style configuration
>>> configuration = SegformerConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model from the nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512 style configuration
>>> model = SegformerModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configSegformerFeatureExtractor
Preprocesses a batch of images and optionally segmentation maps.
Overrides the __call__ method of the Preprocessor class so that both images and segmentation maps can be
passed in as positional arguments.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
< source >( outputs target_sizes: typing.Optional[list[tuple]] = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
- outputs (SegformerForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
list[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
list[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic
segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is
specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of SegformerForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
SegformerImageProcessor
class transformers.SegformerImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2> do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None do_reduce_labels: bool = False **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specified(size["height"], size["width"]). Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - size (
dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"height" -- 512, "width": 512}): Size of the output image after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by theresampleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255. Can be overridden by thedo_reduce_labelsparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a Segformer image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] segmentation_maps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor'], NoneType] = None do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None resample: Resampling = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None do_reduce_labels: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None )
Parameters
- images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - segmentation_maps (
ImageInput, optional) — Segmentation map to preprocess. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image afterresizeis applied. - resample (
int, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling, Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1]. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation. - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_reduce_labels) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
< source >( outputs target_sizes: typing.Optional[list[tuple]] = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
- outputs (SegformerForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
list[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
list[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic
segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is
specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of SegformerForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
SegformerImageProcessorFast
class transformers.SegformerImageProcessorFast
< source >( **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.segformer.image_processing_segformer_fast.SegformerFastImageProcessorKwargs] )
Constructs a fast Segformer image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] segmentation_maps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor'], NoneType] = None **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.segformer.image_processing_segformer_fast.SegformerFastImageProcessorKwargs] ) → <class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
Parameters
- images (
Union[PIL.Image.Image, numpy.ndarray, torch.Tensor, list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']]) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - segmentation_maps (
ImageInput, optional) — The segmentation maps to preprocess. - do_resize (
bool, optional) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
dict[str, int], optional) — Describes the maximum input dimensions to the model. - default_to_square (
bool, optional) — Whether to default to a square image when resizing, if size is an int. - resample (
Union[PILImageResampling, F.InterpolationMode, NoneType]) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional) — Whether to center crop the image. - crop_size (
dict[str, int], optional) — Size of the output image after applyingcenter_crop. - do_rescale (
bool, optional) — Whether to rescale the image. - rescale_factor (
Union[int, float, NoneType]) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — Image mean to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - image_std (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — Image standard deviation to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - do_convert_rgb (
bool, optional) — Whether to convert the image to RGB. - return_tensors (
Union[str, ~utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType]) — Returns stacked tensors if set to `pt, otherwise returns a list of tensors. - data_format (
~image_utils.ChannelDimension, optional) — OnlyChannelDimension.FIRSTis supported. Added for compatibility with slow processors. - input_data_format (
Union[str, ~image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType]) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
- device (
torch.device, optional) — The device to process the images on. If unset, the device is inferred from the input images. - disable_grouping (
bool, optional) — Whether to disable grouping of images by size to process them individually and not in batches. If None, will be set to True if the images are on CPU, and False otherwise. This choice is based on empirical observations, as detailed here: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/38157 - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_reduce_labels) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255.
Returns
<class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
- data (
dict) — Dictionary of lists/arrays/tensors returned by the call method (‘pixel_values’, etc.). - tensor_type (
Union[None, str, TensorType], optional) — You can give a tensor_type here to convert the lists of integers in PyTorch/TensorFlow/Numpy Tensors at initialization.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
< source >( outputs target_sizes: typing.Optional[list[tuple]] = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
- outputs (SegformerForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
list[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
list[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic
segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is
specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of SegformerForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
SegformerModel
class transformers.SegformerModel
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (SegformerModel) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Segformer Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using SegformerImageProcessor. See SegformerImageProcessor.call() for details (processor_classuses SegformerImageProcessor for processing images). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SegformerConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The SegformerModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
SegformerDecodeHead
SegformerForImageClassification
class transformers.SegformerForImageClassification
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (SegformerForImageClassification) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
SegFormer Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the final hidden states) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.segformer.modeling_segformer.SegFormerImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using SegformerImageProcessor. See SegformerImageProcessor.call() for details (processor_classuses SegformerImageProcessor for processing images). - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.segformer.modeling_segformer.SegFormerImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.segformer.modeling_segformer.SegFormerImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SegformerConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage. -
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The SegformerForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SegformerForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512")
>>> model = SegformerForImageClassification.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
...SegformerForSemanticSegmentation
class transformers.SegformerForSemanticSegmentation
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (SegformerForSemanticSegmentation) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
SegFormer Model transformer with an all-MLP decode head on top e.g. for ADE20k, CityScapes.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using SegformerImageProcessor. See SegformerImageProcessor.call() for details (processor_classuses SegformerImageProcessor for processing images). - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Ground truth semantic segmentation maps for computing the loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels > 1, a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SegformerConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels, logits_height, logits_width)) — Classification scores for each pixel.The logits returned do not necessarily have the same size as the
pixel_valuespassed as inputs. This is to avoid doing two interpolations and lose some quality when a user needs to resize the logits to the original image size as post-processing. You should always check your logits shape and resize as needed. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, patch_size, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The SegformerForSemanticSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SegformerForSemanticSegmentation
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512")
>>> model = SegformerForSemanticSegmentation.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits # shape (batch_size, num_labels, height/4, width/4)
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 150, 128, 128]