Inference Endpoints (dedicated) documentation
Text Generation Inference (TGI)
Text Generation Inference (TGI)
TGI is a production-grade inference engine built in Rust and Python, designed for high-performance serving of open-source LLMs (e.g. LLaMA, Falcon, StarCoder, BLOOM and many more). The core features that make TGI a good choice are:
- Continuous batching + streaming: Dynamically groups in-flight requests and streams tokens via Server-Sent Events (SSE)
- Optimized attention & decoding: TGI uses Flash Attention, Paged Attention, KV-caching, and custom CUDA kernels for latency and memory efficiency
- Quantization & weight loading speed: Supports quantizations methods like bitsandbytes and GPTQ and uses Safetensors to reduce load times
- Production readiness: Fully OpenAI-compatible
/v1/chator/v1/completionsAPIs, Prometheus metrics, OpenTelemetry tracing, watermarking, logit controls, JSON schema guidance
By default, the TGI version will be the latest available one (with some delay). But you can also specify a different version by changing the container URL
Configuration
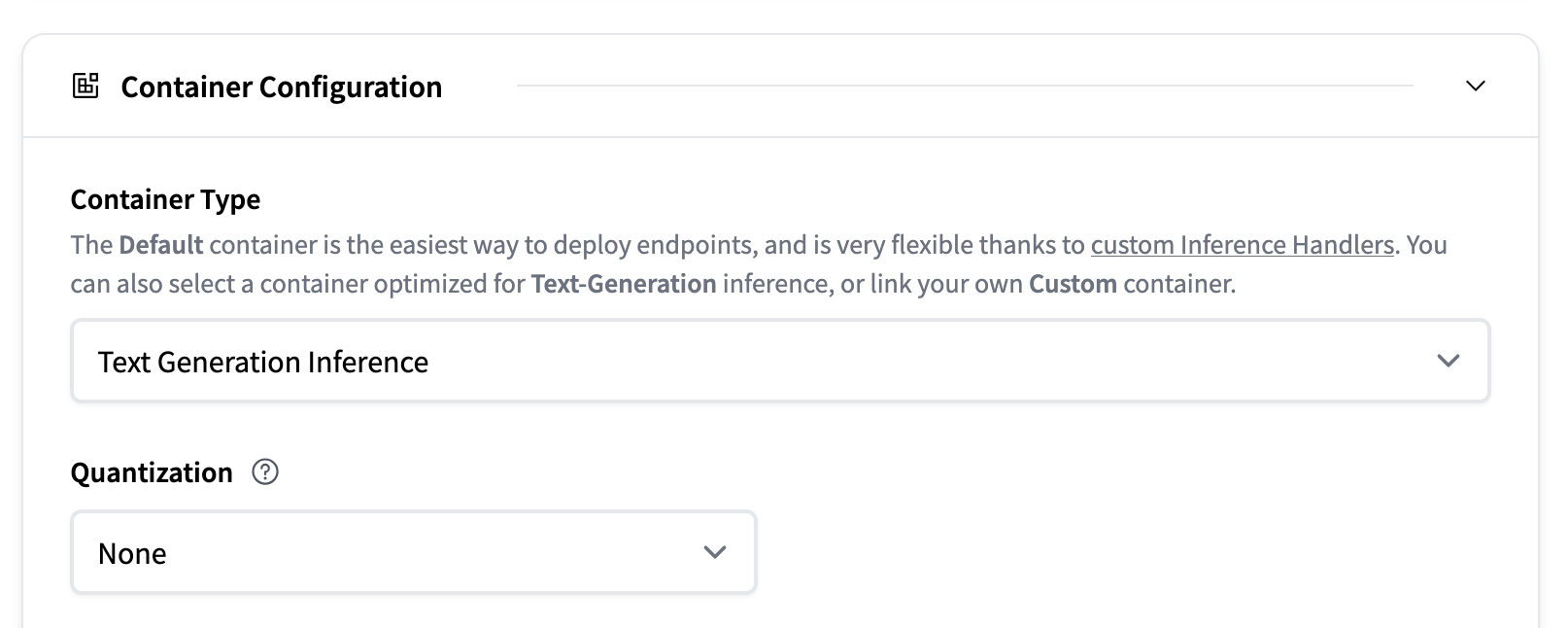
When selecting a model to deploy, the Inference Endpoints UI automatically checks whether a model is supported by TGI. If it is, you’ll see
the option presented under Container Configuration where you can change the following settings:
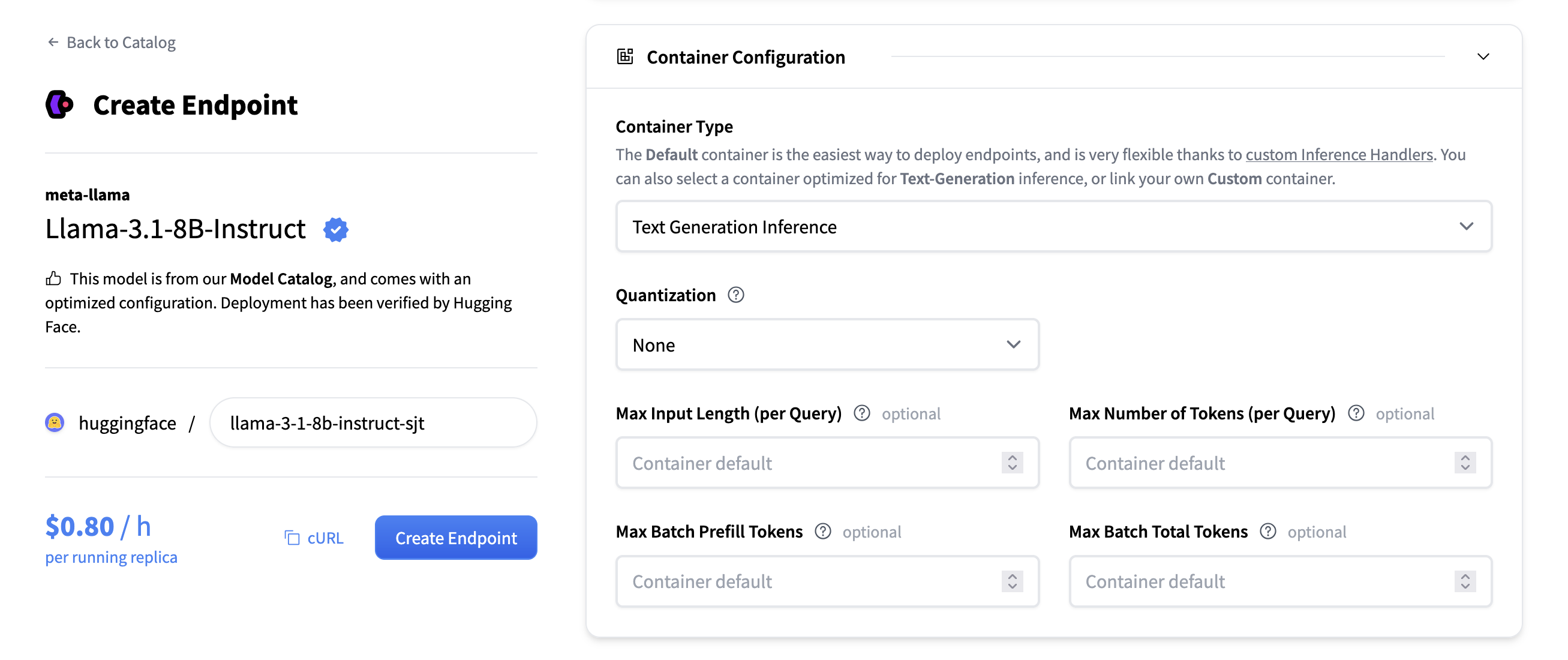
- Quantization: Which quantization method, if any, to use for the model.
- Max Number of Tokens (per query): Changes the maximum amount of tokens a request can contain.
For example a value of
1512means users can send either a prompt of1000tokens and generate512new tokens, or send a prompt of1token and generate1511new tokens. The larger this value, the larger amount each request will be in your RAM and the less effective batching can be. - Max Input Tokens (per query): The maximum number of input tokens, meaning the amount of tokens in the prompt.
- Max Batch Prefill Tokens: Limits the number of tokens for the prefill operation. Prefill tokens are the ones sent in with the user prompt.
- Max Batch Total Tokens: This changes the total amount of potential tokens within a batch. Together with
Max Number of Tokens, this determines how many concurrent requests you can serve. If you setMax Number of Tokensto 100 andMax Batch Total Tokensto 100 as well, you can only serve one request at a time.
In general zero-configuration (see below) is recommended for most cases. TGI supports several other configuration parameters and you’ll find a complete list in the TGI documentation. These can all be set by passing the values as environment variables to the container, link to guide.
Zero configuration
Introduced in TGI v3, the zero-config mode helps you get the most out of your hardware without manual configuration and trial & error. If you leave the values undefined, TGI will on server startup automatically (based on the hardware it’s running on) select the maximal possible values for the max input lenght, max number of tokens, max batch prefill tokens and max batch total tokens. This means that you’ll use your hardware to it’s full capacity.
Supported models
You can find the models that are supported by TGI:
- Browse supported models on the Hugging Face Hub
- In the TGI documentation under the supported models section
- A selection of popular models in the Inference Endpoints Catalog
If a model is supported by TGI, the Inference Endpoints UI will indicate this by disabling/enabling the selection under Container Type configuration.
References
We also recommend reading the TGI documentation for more in-depth information.
< > Update on GitHub